By clicking CONTINUE you are confirming that you are a
Healthcare Professional registered in the UK.
Date of preparation October 2025 UK-GEN-200
Date of preparation October 2025 UK-GEN-199


Tranexamic acid at a dose of 1000mg three times a day for up to 4 days is an effective treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) or menorrhagia.1,2
However… tablet burden can be an issue
• A survey found tranexamic acid adherence can be as low as 33%.3
• The “need to take 2 large tablets three times a day during bleeding” was identified as a barrier for patients.3
See below for full details on dosage, contraindications, precautions and warnings, and side effects.
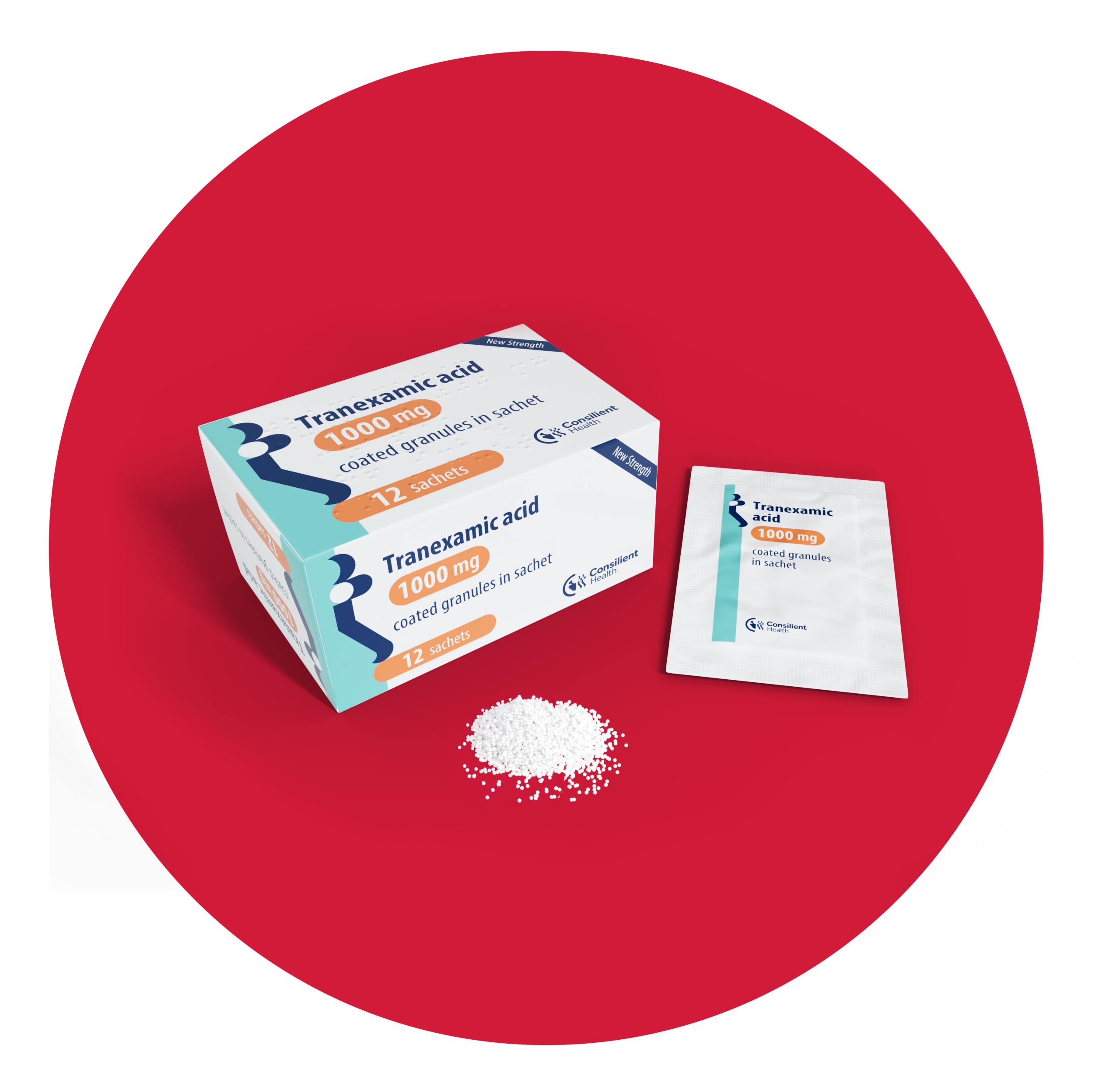
Tranexamic Acid Coated Granules 1000mg vs Tranexamic Acid Tablets 500mg.
See below for full Tranexamic Acid Coated Granules dosage information.
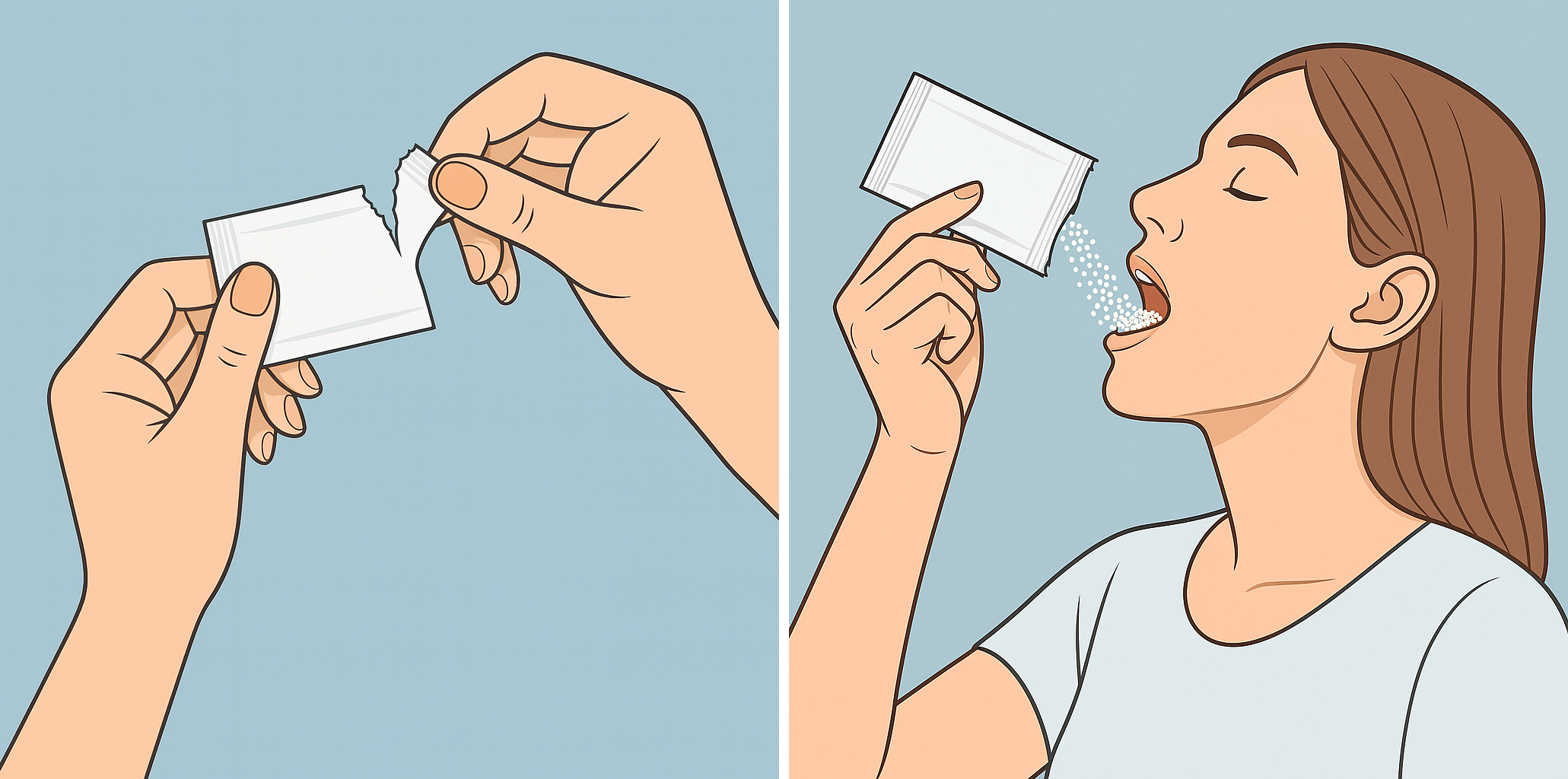
Tranexamic Acid Coated Granules can be swallowed straight from the sachet and, if desired, can be washed down with some water.
It is not needed to mix the granules in food or water and it is recommended not to crush or chew the granules.
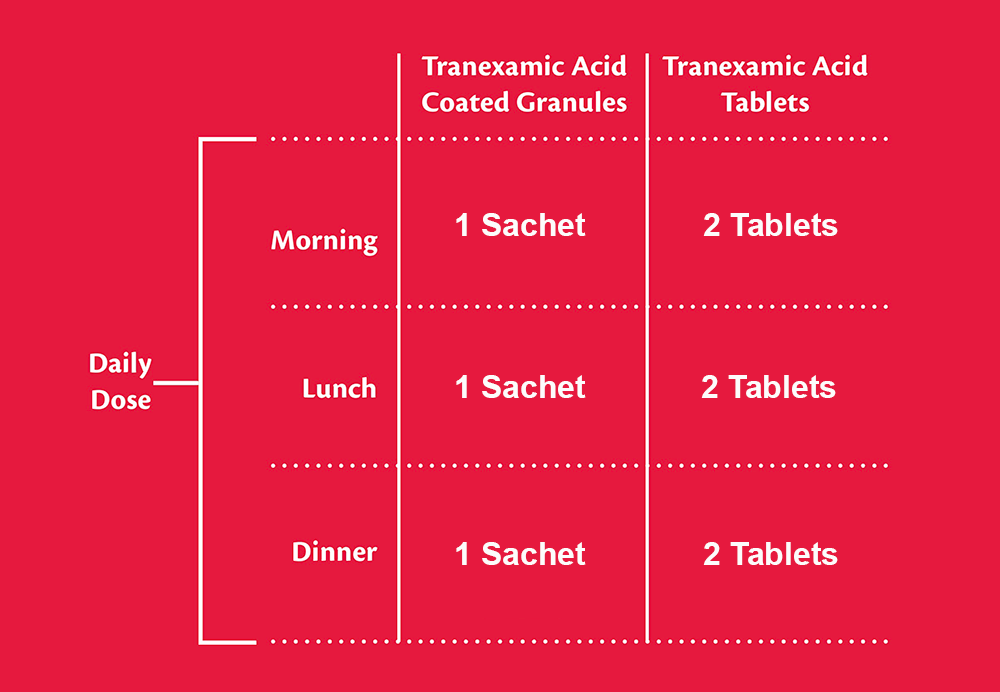
Recommended dosage is 1 sachet 3 times daily as long as needed for up to 4 days (1 sachet every 6 to 8 hours). If very heavy menstrual bleeding, dosage may be increased. A total dose of 4 g daily (4 sachets) should not be exceeded. Treatment with this medicine should not be initiated until menstrual bleeding has started.
Renal impairment: By extrapolation from clearance data relating to the intravenous dosage form, the following reduction in the oral dosage is recommended for patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency.
Serum creatinine (micromole/L) 120-249: Body weight 60kg and above: 15 mg/kg body weight twice daily; Body weight below 60kg: 15 mg/kg body weight once daily.
Serum creatinine (micromole/L) 250-500: Body weight 60kg and above: 15 mg/kg body weight once daily; Body weight below 60kg: 15 mg/kg body weight once every other day.
The maximum dose at each administration in subjects with renal impairment is 1000 mg. Therefore, do not use more than 1 sachet per dose.
Paediatric population: Clinical experience with this medicine in menorrhagic children under 15 years of age is not available.
Before prescribing, please refer to the full Summary of Product Characteristics.
Contraindications
This medicine for menorrhagia is contraindicated in women with: Active thromboembolic disease, Severe renal impairment (risk of accumulation), History of convulsions, Patients taking combined hormonal contraceptives, Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (Sugar spheres (sucrose, maize starch), Povidone K30 (E1201), Sucralose (E955), Silica colloidal anhydrous (E551), Polyacrylate dispersion 30 per cent, Talc (E553B)).
Warnings and precautions
Patients with irregular menstrual bleeding should not use this medicine until the cause of irregular bleeding has been established. If menstrual bleeding is not adequately reduced by this medicine, an alternative treatment should be considered. Patients with a previous thromboembolic event and a family history of thromboembolic disease (patients with thrombophilia) should use this medicine only if there is a strong medical indication and under strict medical supervision. Patients experiencing heavy bleeding during hormonal contraceptive use should not start treatment with tranexamic acid, but are advised to contact their Healthcare Professional. The blood levels are increased in patients with renal insufficiency. Therefore a dose reduction is recommended. The use of tranexamic acid in cases of increased fibrinolysis due to disseminated intravascular coagulation is not recommended. In haematuria from the upper urinary tract clot formation can, in a few cases, lead to ureteric obstruction. Convulsions: Cases of convulsions have been reported in association with tranexamic acid treatment, most of these cases were reported following intravenous injection in high doses. Excipients: This medicinal product contains sucrose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance, glucosegalactose malabsorption or sucrase-isomaltase insufficiency should not take this medicine.
Full list of excipients: Sugar spheres (sucrose, maize starch), Povidone K30 (E1201), Sucralose (E955), Silica colloidal anhydrous (E551), Polyacrylate dispersion 30 per cent, Talc (E553B)
Pregnancy
Should not be used during pregnancy.
Breast feeding
Tranexamic acid is excreted in breast milk, but a risk for an impact on the child seems unlikely at therapeutic doses. Breastfeeding can therefore be continued during this medicine therapy.
Fertility
No data.
Dose-dependent gastrointestinal discomfort is the most commonly reported undesirable effect, but it is usually of mild and temporary nature.
Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10): Dizziness, Headache, Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Nausea, Abdominal pain.
Uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100): Allergic skin reaction.
Frequency not known: Convulsions, Impaired colour vision and other visual disturbances, Thromboembolic events.
For further information the Tranexamic Acid Coated Granules SmPC and PIL can be found below:

Tranexamic Acid Coated Granules are designed to suit the needs of modern women struggling with Tranexamic Acid tablets
References:
UK-GEN-202 November 2025
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/. Adverse events should also be reported to Consilient Health (UK) Ltd, No. 1 Church Road, Richmond upon Thames, Surrey TW9 2QE UK or drugsafety@consilienthealth.com
Copyrights © 2025 All Rights Reserved by Consilient Health Ltd
UK-GEN-202 November 2025